Vicente Tofiño the classic Spanish cartographer of reference
Vicente Tofiño the classic Spanish cartographer of reference
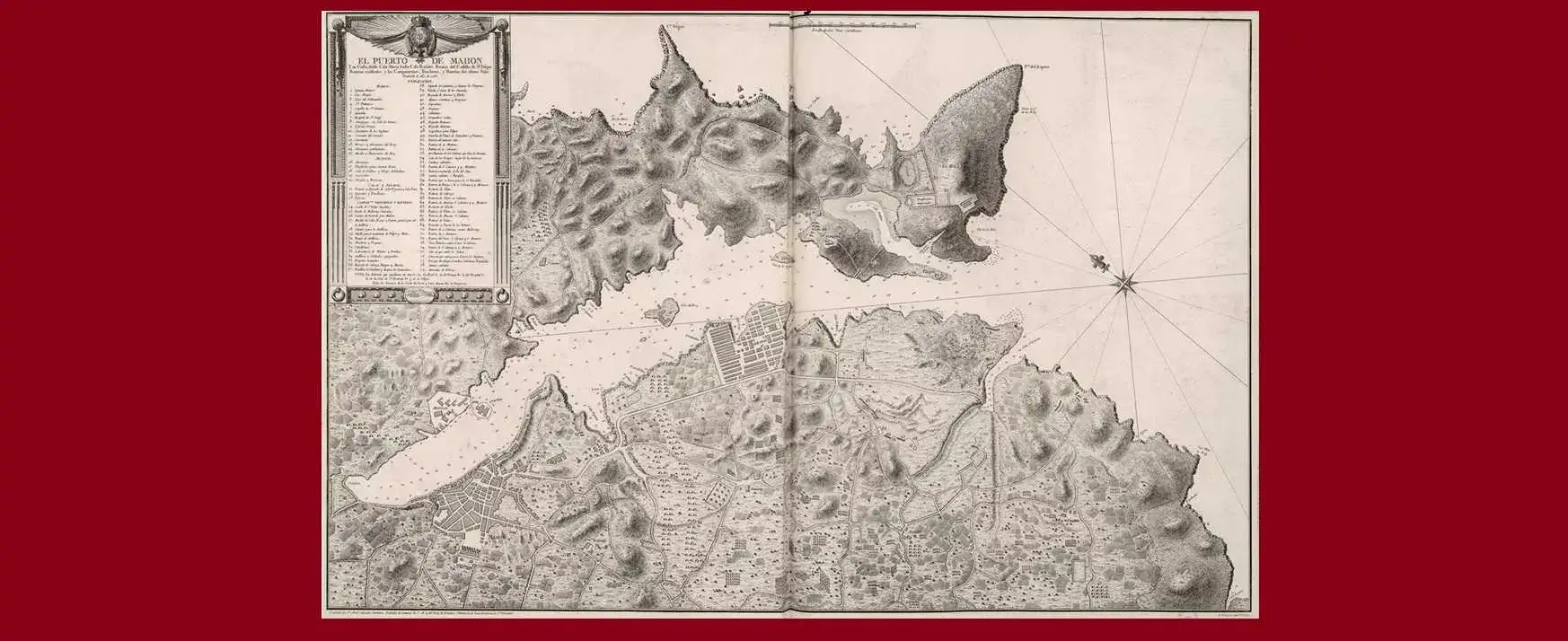
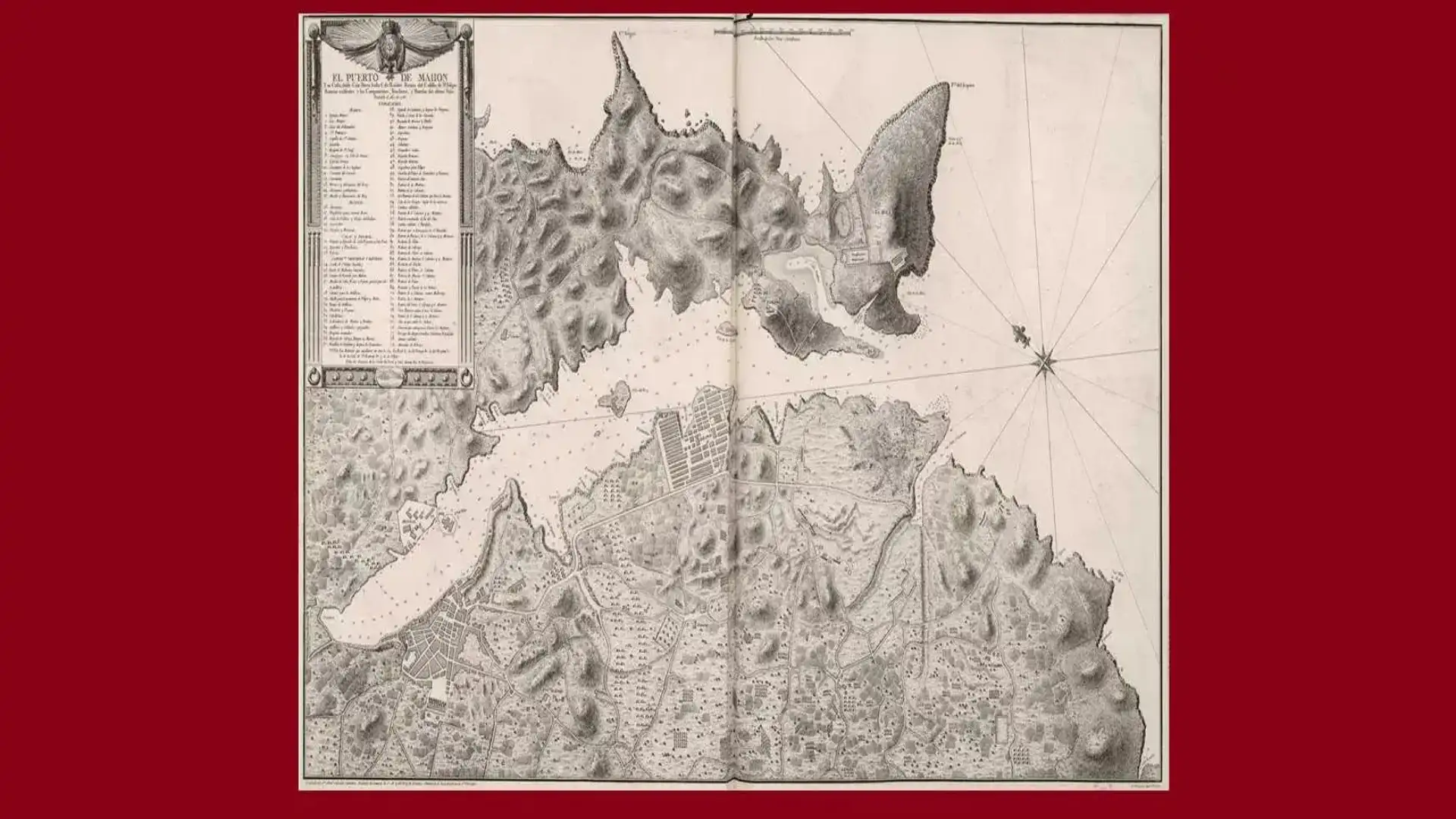
The most relevant work of Tofiño: the Atlas Marítimo de España, published in 1789
Vicente Tofiño de San Miguel, a Gaditano of pure strain, born in 1732, of a marine profession and cosmograph, was Director of the academies of marine guards of Cadiz, El Ferrol and Cartagena, participated in the expedition against Algiers (1773) and on the site of Gibraltar (1782). He is the author of aMarine Atlas of Spain, Azores Islands and Adjacent(1765-1788), he also dedicated himself to the study of mathematics and wrote aElementary geometry treaty. It also published aCollection of spherical cards from the coasts of Spain and Africa, plans and views (1788). To talk about Spanish cartography without mentioning it is an impossible task.
Orphan at the age of 12, Vicente Tofiño de San Miguel set up a cadet in the Guards Company in 1747. In 1750 he applied to be transferred to the Murcia regiment, where he ascended to deputy lieutenant (1752) and deputy lieutenant (1754). With this degree he went to the regiment of Soria and in Segovia was able to treat Father Isla, with whom he perfected his knowledge. He returned to his hometown to occupy a chair of mathematics at the Royal Academy of Marine Guards in Cadiz (1755); shortly after he passed to the Navy as an Ensign of Navio (1757), and ascended to lieutenant in 1767. In 1768 he was appointed director of the aforementioned Academy of Marine Guards, in 1773 he participated in the expedition against Algiers, and in 1776, recently promoted to captain, he directed the academies of El Ferrol (A Coruña) and Cartagena (Murcia). The promotion of Tofiño continued in the following years (Brigadier in 1784, head of squadron in 1789), while its prestige as an astronomer spread throughout Europe.
Among his observations is the one of the overt eclipse of the sun (1764) and the one of the passage of Venus through the Sun (1769), described by the famous French astronomer Joseph J. Lalande in the second edition of hisAstronomie(1771). Other French astronomers, such as Pingré, Borda or Verdun de la Crenne, visited Tofiño at his Gaditan observatory and praised him in his travel relations. From his practices with the students came a whole generation of astronomers (Mazarrodo, Vargas Ponce, Alcalá Galiano, etc.) who helped him in the great work that Antonio Valdés, Minister of Marina, entrusted him in 1783: mapping the coasts of Spain after the scientific work carried out by Jorge Juan and Antonio de Ulloa.
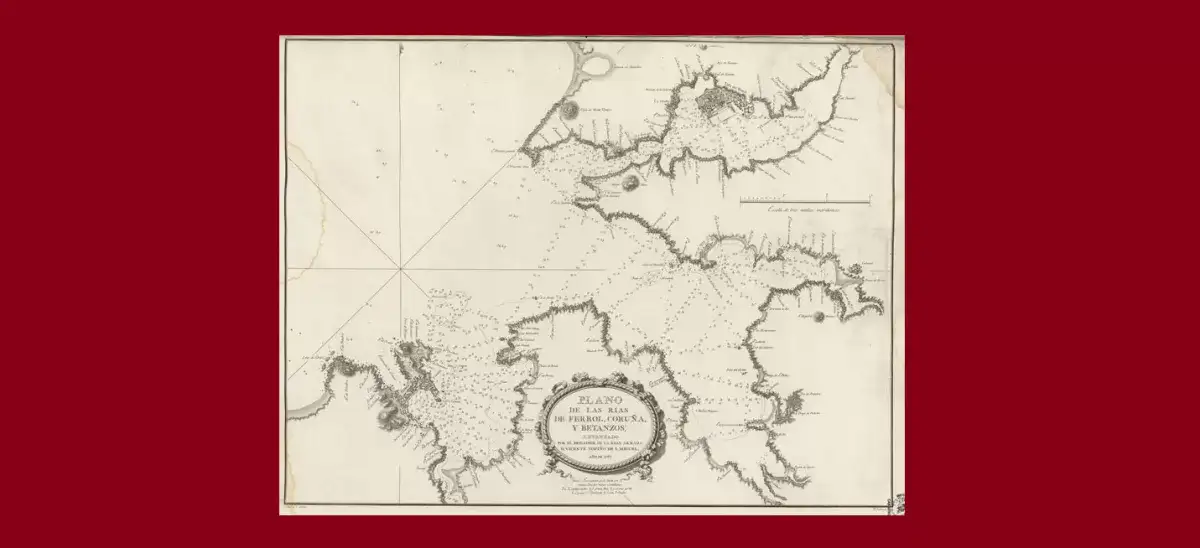
This plane of the Artabre Gulf of Galicia was raised by Tofiño in the year 1787
Thus, after participating in the bombing of Gibraltar (1782) as an assistant to the Duke of Grillón, Vicente Tofiño de San Miguel undertook his famous expeditions (1783-1788) on board the frigate Santa Perpetua and the Bergantines Vivo and Natalia. The result was the Dealer of the coasts of Spain in the Mediterranean and its corresponding of Africa(1787) and that which would be defined as the first work of modern Spanish cartography:Dealer of the coasts of Spain in the Atlantic Ocean and the Azores or Tercers Islands, for intelligence and use of spherical cards(1789). It is also owed aAtlas Marítimo de España(1789) and a collection of spherical letters held by the National Library of Madrid. Illustrated, a prototype of a soldier-scientist, Vicente Tofiño was the real renovator of Spanish cartography in the 18th century; his works were effective until well into the 20th century.
© 2024 Nautica Digital Europe - www.nauticadigital.eu











